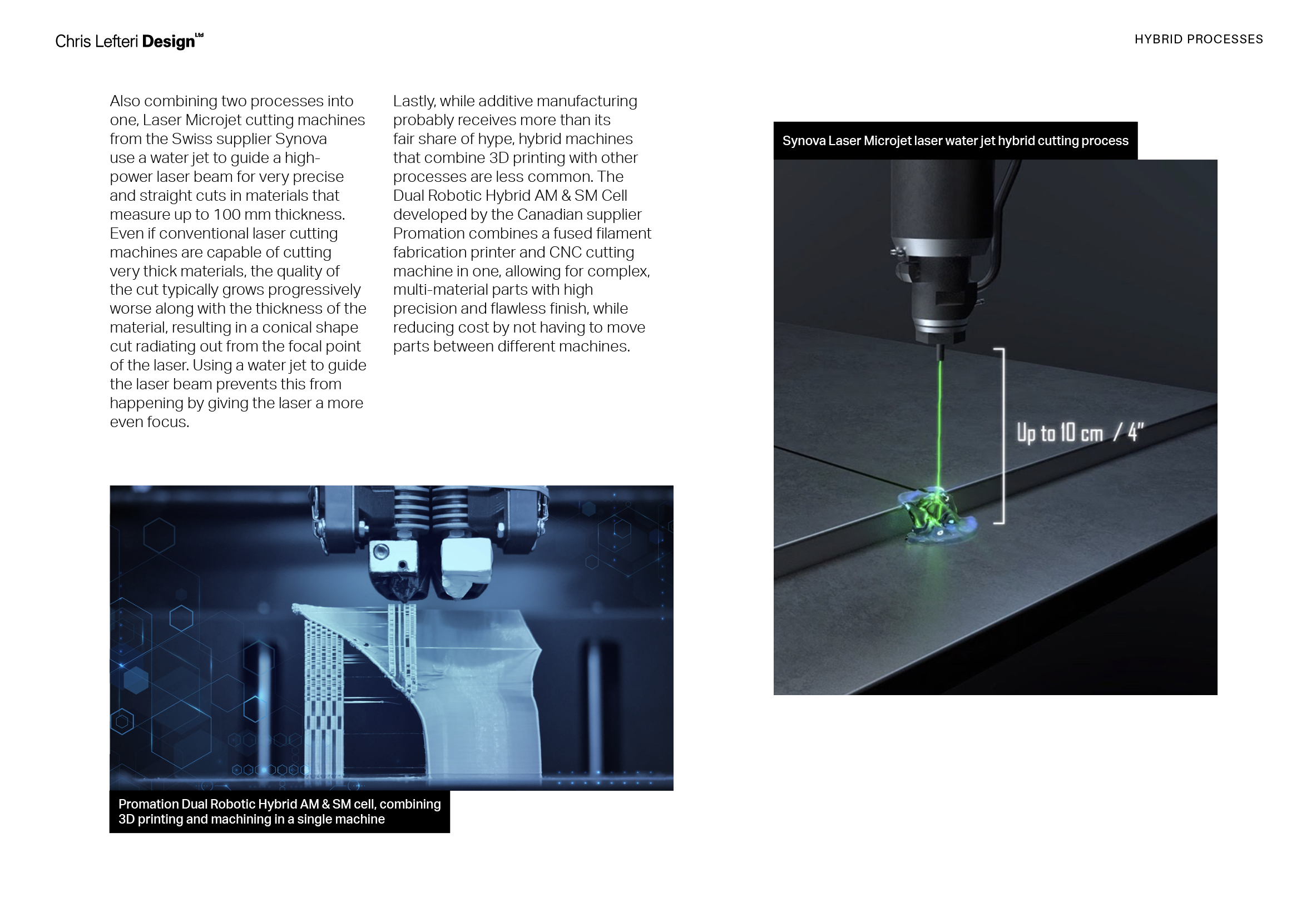
Image 1 of 4
Image 1 of 4

 Image 2 of 4
Image 2 of 4

 Image 3 of 4
Image 3 of 4

 Image 4 of 4
Image 4 of 4





2025+ THE LANDSCAPE OF LEATHER
With no sign of an end to the intense and heated debate around the use of leather, clear and balanced guidance on the environmental and ethical implications of this mainstay of the materials world is more important than ever. In this report, we examine potential approaches to the many challenges and opportunities related to leather:
Responsible finishes: Leather processing continues to be a source of pollution in many manufacturing hot spots around the world, but environmentally responsible alternatives are becoming the norm.
Progressive raw materials: A new generation of leather suppliers is re-evaluating raw materials that were previously rejected or ignored altogether.
Circular leather: Leather recycling is a growing industry that uses both post-industrial scrap and recovered post-consumer leather waste.
Synthetic biology: Several biotech startups are developing lab-grown leathers to avoid potential ethical and environmental implications related to the livestock industry.
Processing efficiency: AI and machine learning are new tools for addressing the inconsistencies that a natural material like leather inevitably presents in terms of colour, pattern, and irregularly shaped hides.
Beyond leather: From transparent and conductive leather to innovative building materials, hides unsuitable for leather production are finding new uses.
£ 500,00
With no sign of an end to the intense and heated debate around the use of leather, clear and balanced guidance on the environmental and ethical implications of this mainstay of the materials world is more important than ever. In this report, we examine potential approaches to the many challenges and opportunities related to leather:
Responsible finishes: Leather processing continues to be a source of pollution in many manufacturing hot spots around the world, but environmentally responsible alternatives are becoming the norm.
Progressive raw materials: A new generation of leather suppliers is re-evaluating raw materials that were previously rejected or ignored altogether.
Circular leather: Leather recycling is a growing industry that uses both post-industrial scrap and recovered post-consumer leather waste.
Synthetic biology: Several biotech startups are developing lab-grown leathers to avoid potential ethical and environmental implications related to the livestock industry.
Processing efficiency: AI and machine learning are new tools for addressing the inconsistencies that a natural material like leather inevitably presents in terms of colour, pattern, and irregularly shaped hides.
Beyond leather: From transparent and conductive leather to innovative building materials, hides unsuitable for leather production are finding new uses.
£ 500,00